Paint Overview
Anytime you draw something in Skia, and want to specify what color it is, or how it blends with the background, or what style or font to draw it in, you specify those attributes in a paint.
Unlike Canvas, paints do not maintain an internal stack of state
(i.e. there is no save/restore on a paint). However, paints are relatively
light-weight, so the client may create and maintain any number of paint objects,
each set up for a particular use. Factoring all of these color and stylistic
attributes out of the canvas state, and into (multiple) paint objects, allows
canvas’ save/restore to be that much more efficient, as all they have to do is
maintain the stack of matrix and clip settings.
paint1 = skia.Paint(
AntiAlias=True,
Color=skia.Color(255, 0, 0),
Style=skia.Paint.kFill_Style)
paint2 = skia.Paint(
AntiAlias=True,
Color=skia.Color(0, 136, 0),
Style=skia.Paint.kStroke_Style,
StrokeWidth=3)
paint3 = skia.Paint(
AntiAlias=True,
Color=skia.Color(136, 136, 136))
blob1 = skia.TextBlob("Skia!", skia.Font(None, 64.0, 1.0, 0.0))
blob2 = skia.TextBlob("Skia!", skia.Font(None, 64.0, 1.5, 0.0))
canvas.clear(skia.ColorWHITE)
canvas.drawTextBlob(blob1, 20.0, 64.0, paint1)
canvas.drawTextBlob(blob1, 20.0, 144.0, paint2)
canvas.drawTextBlob(blob2, 20.0, 224.0, paint3)

This shows three different paints, each set up to draw in a different style. Now the caller can intermix these paints freely, either using them as is, or modifying them as the drawing proceeds.
fillPaint = skia.Paint()
strokePaint = skia.Paint(
Style=skia.Paint.kStroke_Style,
StrokeWidth=3.0
)
canvas.drawRect(skia.Rect.MakeXYWH(10, 10, 60, 20), fillPaint)
canvas.drawRect(skia.Rect.MakeXYWH(80, 10, 60, 20), strokePaint)
strokePaint.setStrokeWidth(5.0)
canvas.drawOval(skia.Rect.MakeXYWH(150, 10, 60, 20), strokePaint)
blob = skia.TextBlob("SKIA", skia.Font(None, 80))
fillPaint.setColor(skia.ColorSetARGB(0xFF, 0xFF, 0x00, 0x00))
canvas.drawTextBlob(blob, 20, 120, fillPaint)
fillPaint.setColor(skia.ColorSetARGB(0xFF, 0x00, 0x00, 0xFF))
canvas.drawTextBlob(blob, 20, 220, fillPaint)

Beyond simple attributes such as color, strokes, and text values, paints support effects. These are subclasses of different aspects of the drawing pipeline, that when referenced by a paint (each of them is reference-counted), are called to override some part of the drawing pipeline.
For example, to draw using a gradient instead of a single color, assign a
Shader to the paint.
paint = skia.Paint(
Shader=skia.GradientShader.MakeLinear(
points=[(0.0, 0.0), (256.0, 256.0)],
colors=[0xFF0000FF, 0xFFFFFF00]))
canvas.drawPaint(paint)

Now, anything drawn with that paint will be drawn with the gradient specified in
the call to MakeLinear().
There are 6 types of effects that can be assigned to a paint:
PathEffect - modifications to the geometry (path) before it generates an alpha mask (e.g. dashing)
ImageFilter - composing custom mask layers (e.g. shadows)
MaskFilter - modifications to the alpha mask before it is colorized and drawn (e.g. blur)
Shader - e.g. gradients (linear, radial, sweep), bitmap patterns (clamp, repeat, mirror)
ColorFilter - modify the source color(s) before applying the xfermode (e.g. color matrix)
Xfermode - e.g. porter-duff transfermodes, blend modes
Paints also hold a reference to a Typeface. The typeface represents a specific font style, to be used for measuring and drawing text. Speaking of which, paints are used not only for drawing text, but also for measuring it:
paint.measureText(...)
paint.getTextBounds(...)
paint.textToGlyphs(...)
paint.getFontMetrics(...)
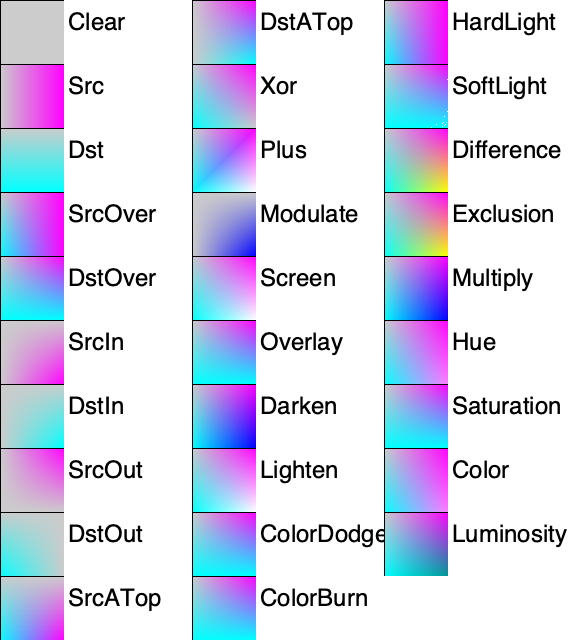
Xfermode
The following example demonstrates all of the Skia’s standard transfer modes. In this example the source is a solid magenta color with a horizontal alpha gradient and the destination is a solid cyan color with a vertical alpha gradient.
def draw_utf8_string(canvas, text, x, y, font, paint):
canvas.drawTextBlob(skia.TextBlob(text, font), x, y, paint)
modes = [
skia.BlendMode.kClear,
skia.BlendMode.kSrc,
skia.BlendMode.kDst,
skia.BlendMode.kSrcOver,
skia.BlendMode.kDstOver,
skia.BlendMode.kSrcIn,
skia.BlendMode.kDstIn,
skia.BlendMode.kSrcOut,
skia.BlendMode.kDstOut,
skia.BlendMode.kSrcATop,
skia.BlendMode.kDstATop,
skia.BlendMode.kXor,
skia.BlendMode.kPlus,
skia.BlendMode.kModulate,
skia.BlendMode.kScreen,
skia.BlendMode.kOverlay,
skia.BlendMode.kDarken,
skia.BlendMode.kLighten,
skia.BlendMode.kColorDodge,
skia.BlendMode.kColorBurn,
skia.BlendMode.kHardLight,
skia.BlendMode.kSoftLight,
skia.BlendMode.kDifference,
skia.BlendMode.kExclusion,
skia.BlendMode.kMultiply,
skia.BlendMode.kHue,
skia.BlendMode.kSaturation,
skia.BlendMode.kColor,
skia.BlendMode.kLuminosity,
]
rect = skia.Rect(64.0, 64.0)
font = skia.Font(None, 24)
stroke = skia.Paint(Style=skia.Paint.kStroke_Style)
src = skia.Paint(
Shader=skia.GradientShader.MakeLinear(
[(0.0, 0.0), (64.0, 0.0)],
[skia.ColorMAGENTA & 0x00FFFFFF, skia.ColorMAGENTA]))
dst = skia.Paint(
Shader=skia.GradientShader.MakeLinear(
[(0.0, 0.0), (0.0, 64.0)],
[skia.ColorCYAN & 0x00FFFFFF, skia.ColorCYAN]))
canvas.clear(skia.ColorWHITE)
N = len(modes)
K = (N - 1) // 3 + 1
assert K * 64 >= 640, "Not tall enough"
for i in range(N):
with skia.AutoCanvasRestore(canvas):
canvas.translate(192.0 * (i // K), 64.0 * (i % K))
desc = skia.BlendMode_Name(modes[i])
draw_utf8_string(canvas, desc, 68.0, 30.0, font, skia.Paint())
canvas.clipRect(skia.Rect(64.0, 64.0))
canvas.drawColor(skia.ColorLTGRAY)
canvas.saveLayer()
canvas.clear(skia.ColorTRANSPARENT)
canvas.drawPaint(dst)
src.setBlendMode(modes[i])
canvas.drawPaint(src)
canvas.drawRect(rect, stroke)
Shader
Several shaders are defined (besides the linear gradient already mentioned):
Bitmap Shader
image = skia.Image.MakeFromEncoded(
skia.Data.MakeFromFileName('../skia/resources/images/color_wheel.png'))
canvas.clear(skia.ColorWHITE)
matrix = skia.Matrix()
matrix.setScale(0.75, 0.75)
matrix.preRotate(30.0)
canvas.drawPaint({
'Shader': image.makeShader(
skia.TileMode.kRepeat,
skia.TileMode.kRepeat,
matrix
)
})
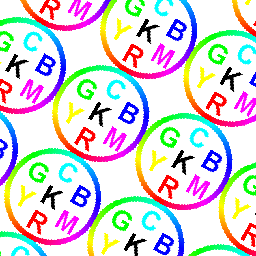
Radial Gradient Shader
canvas.drawPaint({
'Shader': skia.GradientShader.MakeRadial(
center=(128.0, 128.0),
radius=180.0,
colors=[skia.ColorBLUE, skia.ColorYELLOW]
)
})

Two-Point Conical Gradient Shader
canvas.drawPaint({
'Shader': skia.GradientShader.MakeTwoPointConical(
start=(128.0, 128.0),
startRadius=128.0,
end=(128.0, 16.0),
endRadius=16.0,
colors=[skia.ColorBLUE, skia.ColorYELLOW]
)
})

Sweep Gradient Shader
canvas.drawPaint({
'Shader': skia.GradientShader.MakeSweep(
cx=128.0,
cy=128.0,
colors=[
skia.ColorCYAN,
skia.ColorMAGENTA,
skia.ColorYELLOW,
skia.ColorCYAN
]
)
})

Fractal Perlin Noise Shader
canvas.drawPaint({
'Shader': skia.PerlinNoiseShader.MakeFractalNoise(0.05, 0.05, 4, 0.0)
})
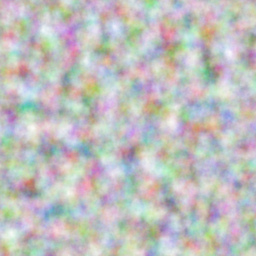
Turbulence Perlin Noise Shader
canvas.drawPaint({
'Shader': skia.PerlinNoiseShader.MakeTurbulence(0.05, 0.05, 4, 0.0)
})
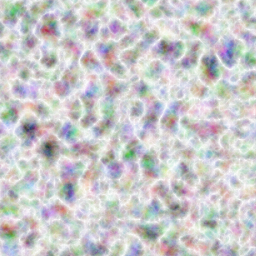
Compose Shader
shader = skia.Shaders.Blend(
skia.BlendMode.kDifference,
skia.GradientShader.MakeRadial((128.0, 128.0), 180.0, [skia.ColorBLUE, skia.ColorYELLOW]),
skia.PerlinNoiseShader.MakeTurbulence(0.025, 0.025, 2, 0.0))
canvas.drawPaint({'Shader': shader})
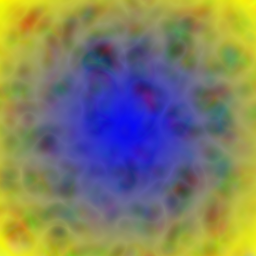
ImageFilter
See ImageFilters for a list of available filters.
Drop Shadow
canvas.drawColor(skia.ColorWHITE)
paint = skia.Paint(
ImageFilter=skia.ImageFilters.DropShadow(3, 3, 5, 5, skia.ColorBLACK)
)
blob = skia.TextBlob("Skia", skia.Font(None, 120))
canvas.drawTextBlob(blob, 0, 160, paint)

Dilate
canvas.drawColor(skia.ColorWHITE)
paint = skia.Paint(
ImageFilter=skia.ImageFilters.Dilate(2, 2)
)
blob = skia.TextBlob("Skia", skia.Font(None, 120))
canvas.drawTextBlob(blob, 0, 160, paint)

Erode
canvas.drawColor(skia.ColorWHITE)
paint = skia.Paint(
ImageFilter=skia.ImageFilters.Erode(2, 2)
)
blob = skia.TextBlob("Skia", skia.Font(None, 120))
canvas.drawTextBlob(blob, 0, 160, paint)

MaskFilter
Blur Mask Filter
canvas.drawColor(skia.ColorWHITE)
paint = skia.Paint(
MaskFilter=skia.MaskFilter.MakeBlur(skia.kNormal_BlurStyle, 5.0)
)
blob = skia.TextBlob("Skia", skia.Font(None, 120))
canvas.drawTextBlob(blob, 0, 160, paint)

ColorFilter
Color Matrix Color Filter
image = skia.Image.MakeFromEncoded(
skia.Data.MakeFromFileName(
'../skia/resources/images/mandrill_512_q075.jpg'))
def f(canvas, x, y, colorMatrix):
canvas.drawImage(image, x, y, skia.Paint(
ColorFilter=skia.ColorFilters.Matrix(colorMatrix),
))
canvas.scale(0.25, 0.25)
colorMatrix = [
0, 1, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 1, 0, 0,
1, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 1, 0
]
f(canvas, 0, 0, colorMatrix)
grayscale = [
0.21, 0.72, 0.07, 0.0, 0.0,
0.21, 0.72, 0.07, 0.0, 0.0,
0.21, 0.72, 0.07, 0.0, 0.0,
0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0
]
f(canvas, 512, 0, grayscale)

Color Table Color Filter
canvas.scale(0.5, 0.5)
ct = bytearray(256)
for i in range(256):
x = (i - 96) * 255 // 64
ct[i] = min(255, max(0, x))
paint = skia.Paint(
ColorFilter=skia.TableColorFilter.MakeARGB(None, ct, ct, ct)
)
canvas.drawImage(image, 0, 0, paint)

PathEffect
Path 2D Path Effect
Stamp the specified path to fill the shape, using the matrix to define the latice.
scale = 10.0
path = skia.Path()
pts = [2, 2, 1, 3, 0, 3, 2, 1, 3, 1, 4, 0, 4, 1,
5, 1, 4, 2, 4, 3, 2, 5, 2, 4, 3, 3, 2, 3]
path.moveTo(2 * scale, 3 * scale)
for i in range(0, len(pts), 2):
path.lineTo(pts[i] * scale, pts[i + 1] * scale)
path.close()
matrix = skia.Matrix.MakeScale(4 * scale, 4 * scale)
paint = skia.Paint(
AntiAlias=True,
PathEffect=skia.Path2DPathEffect.Make(matrix, path),
)
canvas.clear(skia.ColorWHITE)
bounds = skia.Rect(-4 * scale, -4 * scale, 256, 256)
canvas.drawRect(bounds, paint)
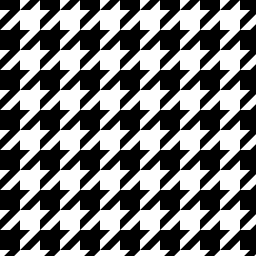
Line 2D Path Effect
A special case of Path2DPathEffect where the path is a straight line to be stroked, not a path to be filled.
lattice = skia.Matrix()
lattice.setScale(8.0, 8.0)
lattice.preRotate(30.0)
paint = skia.Paint(
AntiAlias=True,
PathEffect=skia.Line2DPathEffect.Make(0.0, lattice)
)
bounds = skia.Rect(256, 256)
bounds.outset(8.0, 8.0)
canvas.clear(skia.ColorWHITE)
canvas.drawRect(bounds, paint)
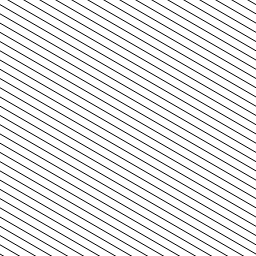
Path 1D Path Effect
Create dash-like effects by replicating the specified path along the drawn path.
path = skia.Path()
path.addOval(skia.Rect(16.0, 6.0))
paint = skia.Paint(
AntiAlias=True,
PathEffect=skia.Path1DPathEffect.Make(
path, 32.0, 0.0, skia.Path1DPathEffect.kRotate_Style),
)
canvas.clear(skia.ColorWHITE)
canvas.drawCircle(128.0, 128.0, 122.0, paint)
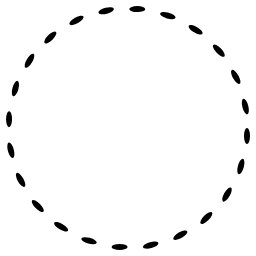
Corner Path Effect
A path effect that can turn sharp corners into various treatments (e.g. rounded corners).
def star():
from math import cos, sin
R, C = 115.2, 128.0
path = skia.Path()
path.moveTo(C + R, C)
for i in range(1, 7):
a = 2.6927937 * i
path.lineTo(C + R * cos(a), C + R * sin(a))
path.close()
return path
paint = skia.Paint(
AntiAlias=True,
PathEffect=skia.CornerPathEffect.Make(32.0),
Style=skia.Paint.kStroke_Style,
)
canvas.clear(skia.ColorWHITE)
path = star()
canvas.drawPath(path, paint)
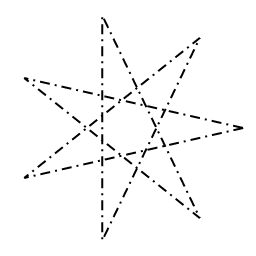
Dash Path Effect
A path effect that implements dashing.
paint = skia.Paint(
AntiAlias=True,
PathEffect=skia.DashPathEffect.Make([10.0, 5.0, 2.0, 5.0], 0.0),
StrokeWidth=2.0,
Style=skia.Paint.kStroke_Style,
)
canvas.clear(skia.ColorWHITE)
path = star()
canvas.drawPath(path, paint)
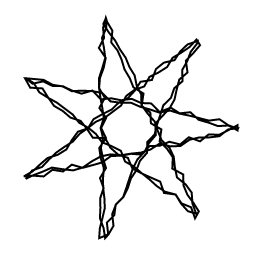
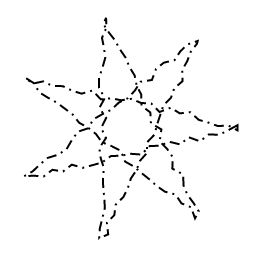
Discrete Path Effect
This path effect chops a path into discrete segments, and randomly displaces them.
paint = skia.Paint(
AntiAlias=True,
PathEffect=skia.DiscretePathEffect.Make(10.0, 4.0),
StrokeWidth=2.0,
Style=skia.Paint.kStroke_Style,
)
canvas.clear(skia.ColorWHITE)
path = star()
canvas.drawPath(path, paint)

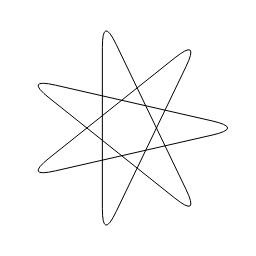
Compose Path Effect
A pathEffect whose effect is to apply first the inner pathEffect and the the outer pathEffect (i.e. outer(inner(path))).
path_effect = skia.PathEffect.MakeCompose(
skia.DashPathEffect.Make([10.0, 5.0, 2.0, 5.0], 0.0),
skia.DiscretePathEffect.Make(10.0, 4.0)
)
paint = skia.Paint(
AntiAlias=True,
PathEffect=path_effect,
StrokeWidth=2.0,
Style=skia.Paint.kStroke_Style,
)
canvas.clear(skia.ColorWHITE)
path = star()
canvas.drawPath(path, paint)
Sum Path Effect
A pathEffect whose effect is to apply two effects, in sequence (i.e. first(path) + second(path)).
path_effect = skia.PathEffect.MakeSum(
skia.DiscretePathEffect.Make(10.0, 4.0),
skia.DiscretePathEffect.Make(10.0, 4.0, 1245)
)
paint = skia.Paint(
AntiAlias=True,
PathEffect=path_effect,
StrokeWidth=2.0,
Style=skia.Paint.kStroke_Style,
)
canvas.clear(skia.ColorWHITE)
path = star()
canvas.drawPath(path, paint)